
Once the logical volumes are created and mounted, you can use them as your normal volumes.

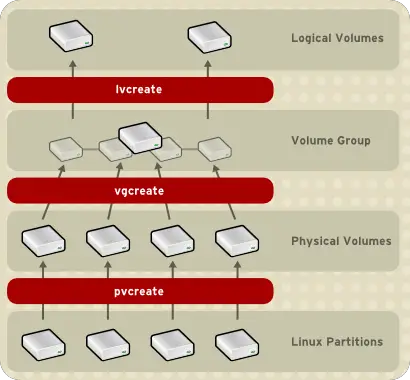
To view the status of the mount, use the mount command. Use the mount command to mount:# mount If you want you mount points to be available after reboot, you can add mount point entries in ‘/etc/fstab’. Please make sure your mount directories already exist. Once the logical volumes are formatted, you can mount them on your mount directories. If you are using the ext4 filesystem:#mkfs.ext4 In our case, it’s:# mkfs.ext4 /dev/n2ws/data # mkfs.ext4 /dev/n2ws/backup Once the logical volumes are created, we can format them using any filesystem like ext4, XFS, and more. Create Logical VolumesOnce the LVM volume group is created, it’s time to create logical volumes.Syntax: sudo lvcreate –name –size In this case, we are creating two logical volumes (data and backup).For data logical volume: For backup logical volume: Once the logical volumes are created, we can view their status using the “lvdisplay” command.There are also commands like “vgscan”, which scan all disks for LVM volume groups. For this, we used the vgcreate command to create a volume group by providing the name of the volume group and the path of actual physical volumes.Syntax: # sudo vgcreate Once the LVM volume group is created, you can use the vgdisplay command to show its attributes. A group of physical volumes or disks are combined together into a single storage file which is referred to as the LVM volume group. Once the devices are initialized, you can create the LVM volume group. Display device attributesFor this, we need to use the pvdisplay command to display information about physical disks.It can either initialize a complete physical disk or a partition on physical disks.Syntax : sudo pvcreate pvcreate is used to initialize disk or partitions that will be used by LVM. Initialize devices to use with the LVMIn order to do this, we need to use the pvcreate command.The EBS volumes are given the following device names: ‘/dev/sdf’, ‘/dev/sdg’ and ‘/dev/sdh’. Attach EBS volumes to your EC2 instanceIn this case, we are attaching three 10GB SSD EBS volumes.LVMs provide the ability to dynamically expand and shrink virtual partitions and make additions to physical volumes on the fly for existing LVMs. You can have multiple virtual partitions on a physical volume or a single virtual partition over multiple physical volumes.

LVMs create an abstraction layer on top of underlying disk layouts and allows sysadmins to create virtual partitions over physical volumes. In this post, we’ll take a deeper look at dynamic disk arrays (i.e., LVM). With multiple EBS volumes, network performance is increased between EC2 instances and EBS volumes. To fix these issues, the organization decides to leverage Logical Volume Managers (LVMs), which provide the option to easily increase the size of their volume by adding more EBS volumes. On top of that, there are network performance bottlenecks between EC2 instances and the EBS volume that impact system performance on the whole.

However, this causes a problem for the organization because shutting down the database server results in lost business. But, every time they increase it, a maintenance window has to be scheduled where the database server is shut down, an EBS snapshot of the data volume is created, and a newer, bigger volume is created and attached to the instance. In terms of storage, the organization has a 1TB EBS volume, which they can increase to 16TB. As the company grows, the size of its database also grows at a rate of 10GB per day. Picture the following scenario: an organization uses EC2 instances for its database where data is stored in EBS volumes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
